200,000+ products from a single source!
sales@angenechem.com
Home > Phenoxy-Dialkoxy Borates as a New Class of Readily Prepared Preactivated Reagents for Base-Free Cross-Coupling
Phenoxy-Dialkoxy Borates as a New Class of Readily Prepared Preactivated Reagents for Base-Free Cross-Coupling
Marco Paladino,[a] Michele Boghi,[a] and Dennis G. Hall
Introduction
Several types of organoboron compounds can be employed as nucleophilic carbon-based reagents in transition metal-catalyzed processes, such as the popular Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction.[1] Typically, the nucleophilic nature of the carbon-boron bond is revealed upon in situ formation of a tetrahedral boron species during the transition-metal-catalyzed reaction. Although many variants of this activation strategy have been exploited successfully, most notably with boronic acids, it still possesses limitations: 1. Often the tetrahedral boronate ion is a transient entity that is not isolated and requires
strongly basic conditions in order to form; 2. Some boronic acids are sensitive to oxidation or protodeboronation, therefore they require careful handling and storage; 3. Boronic acids tend to exist as mixtures containing various proportions of dehydrated anhydrides, such as as the 6-membered boroxines, which makes it challenging to determine their accurate stoichiometry. To address these problems, a number of ′masked′ boronic acids or preactivated adducts have been proposed (Figure 1). For example, air- and bench-stable trifluoroborate salts M[RBF3] (M = K or NR4) are solids that are easy to prepare, handle, and quantify.[2] On the other hand, they tend to display low solubility in many common organic solvents.[3]
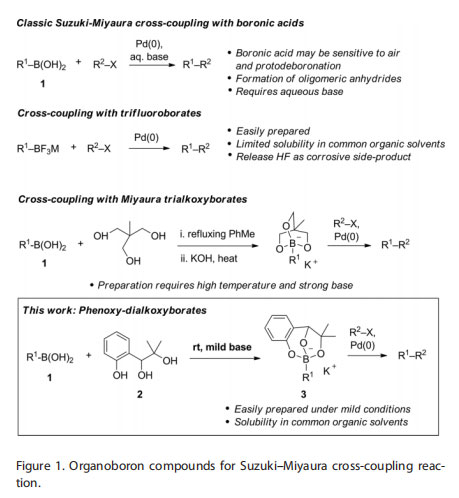
Use of aqueous base is still required for their activation and coupling, and corrosive HF is released in the coupling process. Likewise, MIDA boronates are a stable class of protected boronic acid derivatives but they also require the use of a stoichiometric quantity of base as part of a slow-release mechanism.[4,5] In 2006, Cammidge and co-workers reported the preparation and characterization of discrete trihydroxy borate sodium salts (RB(OH)3– Na+) as isolable and stable reagents for use in the concept of direct base-free Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling.[6]
The absence of base is advantageous, however it is not known whether trihydroxyborate salts are orthogonal with other boron adducts such as trifluoroborate salts. Subsequently, Miyaura and co-workers reported the preparation and characterization of cyclic trialkoxyborates that can also be employed directly in base-free Suzuki–Miyaura cross-couplings and other C–C bondforming reactions (Figure 1).[7,8]
Whereas the reaction conditions for the cross-coupling are mild, the synthesis of the requisite trialkoxyborates from free boronic acids requires high temperatures (refluxing toluene) and a strong base (KOH), which is not ideal for thermosensitive and highly functionalized boronic acids. Consequently, there is a need for new types of stable, preactivated adducts that can be prepared with ease under mild reaction conditions, and that are easy to handle and soluble in most common organic solvents. Herein, we report the design, facile synthesis, and crosscoupling of a new class of phenoxy-dialkoxy adducts (3) of organoboronic acids (1) and triol 2 (Figure 1). These adducts form under ambient conditions, at a significantly lower temperature and with a weaker base compared to the conditions required
for the preparation of trialkoxyborates.
Results and Discussion
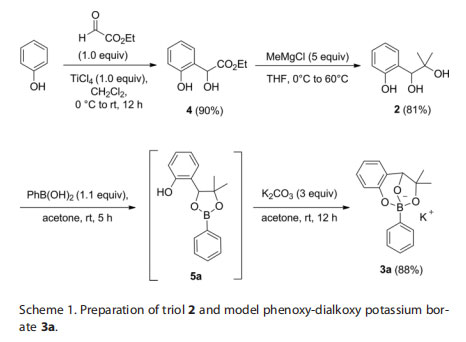
Triol 2 was selected because it possesses several key features for the purpose of this application: 1. It embeds a hindered 1,2-alkanediol group that demonstrates a high affinity for boronic acids; 2. It includes a phenoxy moiety which, with a lower pKa than a regular aliphatic alcohol, will allow a more facile deprotonation and concomitant quaternization of the boron atom;3. The aromatic ring can help increase the solubility of the resulting adducts in organic solvents. Triol 2 is easily synthesized from phenol as shown in Scheme 1. To this end, ortho-hydroxyalkylation with EtO2CCHO (ethyl glyoxalate) furnishes intermediate 4, which is reacted with MeMgCl to give the desired triol2.[9] The preparation of phenoxy-dialkoxy adducts is also straightforward, and the conditions were optimized using phenylboronic acid (Scheme 1). Thus, the boronic acid is condensed with triol 2 at room temperature in acetone, followed by addition of potassium carbonate to yield the desired triolborate 3a in high yield. The reaction is presumed to proceed through the formation of a boronic ester intermediate (e.g. 5a), which is then converted into the corresponding phenoxy-dialkoxy borate by deprotonation of the phenol, and concomitant cyclization with quaternization of the boron atom.
The potassium borate 3a was interchanged into the corresponding ammonium salt 6a, which was recrystallized to provide crystals suitable for X-ray crystallographic analysis (Figure 2).[10] In 6a, the length of the B–O bonds is 1.40–1.53 Å and 1.60 Å for the C–B bond. As expected from the loss of conjugation with the boron atom, these distances are significantly longer than the values observed in boronic acids (1.36–1.37 Å for B–O, and 1.57 Å for C–B)[11a] and pinacol boronic esters (1.31 Å for B–O, and 1.57 Å for C–B).[11b] The tetrahedral nature of the boron atom is clearly depicted in the ORTEP diagram: all of the C–B–O and O–B–O bond angles are relatively close to the expected value of 109 °. Quaternization of the boron center can also be inferred by NMR spectroscopy: 11B-NMR analysis reveals
a characteristic broad signal with upfield chemical shift, ca.δ = 7.5 ppm, typical of a negatively charged tetrahedral boron species.
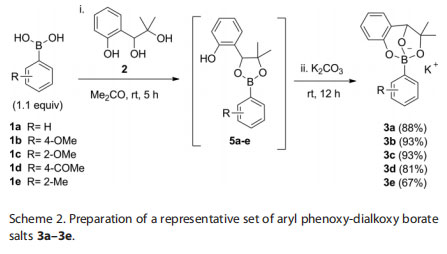
To test the generality of the formation of phenoxy-dialkoxy borates, a prototypical set of arylboronic acids 1a–1e with various electronic and steric characteristics were condensed with triol 2 at room temperature in acetone, followed by addition of potassium carbonate to yield the desired triolborate salts 3a–e in high yields (Scheme 2). Most of the adducts 3a–3e are solids[12] that can be recrystallized with ease from diethyl ether. They are soluble in most organic solvents with the exception of halogenated hydrocarbons (i.e. dichloromethane and chloroform).
The application of phenoxy-dialkoxy boronates in base-free Pd-catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling was assessed using as model substrates the phenyl borate salt 3a and p-iodoanisole(7) (Table 1). The formation of the expected coupling product 8a was optimized by examining the effect of temperature and solvent using Pd(OAc)2 as the pre-catalyst. From the results of Table 1, it is apparent that the reaction does not proceed at room temperature and requires gentle heating to 45 °C in order to reach completion within 18 hours when using triphenylphosphine as the ligand. A variety of solvents are tolerated, making this reaction suitable for both hydrophobic as well as more polar substrates (entries 5–9). As expected, the presence of water is crucial for a successful outcome.[7] Presumably, partial hydrolysis to a monohydroxyborate intermediate is required for an efficient transmetallation step. Initially, PPh3 was used as the ligand and since it gave satisfying results, commercially available Pd(PPh3)4 was selected as the catalyst for the substrate scope study.
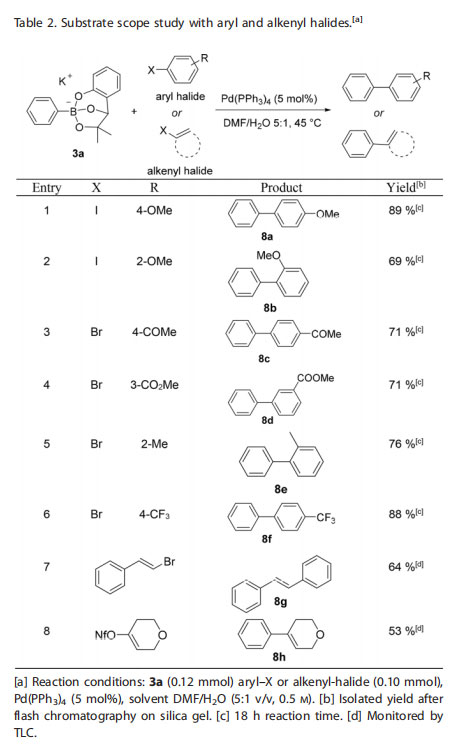
With optimized cross-coupling conditions in hand, different aryl and alkenyl halides were evaluated. Aryl halides with electron-withdrawing or electron-donating substituents both led to a successful cross-coupling with the phenoxy-dialkoxyborate 3a (Table 2). Notably, more congested ortho-substituted aryl halides (entry 2 and entry 5) afforded the expected biphenyl products in good yields. Cross-coupling with alkenyl halides and pseudo-halides was also examined and the corresponding products were isolated in good yields (entry 7 and 8).
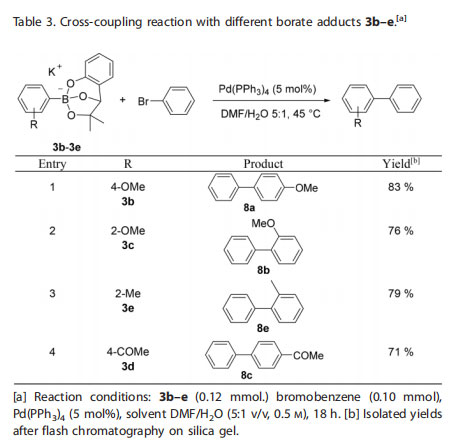
The same procedure was tested in the cross-coupling of a variety of aryl borates 3b–e with bromobenzene (Table 3). The expected biphenyl products were isolated in good yields. Remarkably, the more sterically hindered ortho-substituted aryl borates (entry 2 and 3) successfully underwent the cross-coupling reaction in very good yields. One attractive attribute of this new class of adducts of boronic acids is their potential chemical orthogonality with other boron containing reagents.[13] With this view in mind, we turned our attention to the para-bromoaryl MIDA boronate 9 and trifluoroborate salt 11, with the goal of evaluating their chemoselectivity with the phenoxy-dialkoxy borates. To our satisfaction, bifunctional substrates 9 and 11 underwent the crosscoupling reaction with 3a uneventfully, affording the desired biaryl boron adducts 10 and 12 in good yields (Scheme 3). The slower hydrolysis rate of the MIDA boronate and the requirement of a base to activate the trifluoroborate moiety enables chemoselective cross-coupling conditions where these groups remain unreactive throughout these transformations.
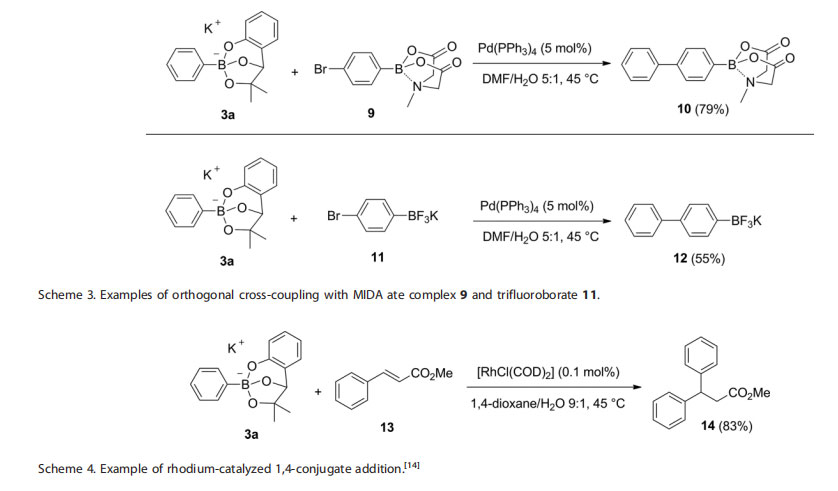
Lastly, with the goal of expanding the application of these new phenoxy-dialkoxy borates to other transition metal-catalyzed transformations, we tested the suitability of aryl borate 3a in a base-free rhodium catalyzed 1,4-conjugate addition.[14] In the event, the reaction with trans-methylcinnamate (13) proceeded smoothly under mild conditions, affording the expected biphenyl product 14 in good yield (Scheme 4).
Conclusions
In summary, we have developed a new class of phenoxy-dialkoxy borate adducts that can be employed as coupling partners in base-free Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. The ease of preparation using a milder base at room temperature along with their solubility in many of the commonly used organic solvents makes these phenoxy-dialkoxy adducts an advantageous alternative for base-sensitive substrates. Moreover, this methodology enables chemoselective cross-coupling reactions with other boron reagents such as MIDA esters and trifluoroborate salts. Finally, it has also been demonstrated that such boron complexes can be used for other base-free metal-catalyzed reactions, such as the rhodium-catalyzed 1,4-conjugate addition. We are planning to further expand the scope and applications
of this new and complementary class of boron reagents.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada (Discovery Grant to D. G. H.). We thank Dr. Michael J. Ferguson (X-ray Crystallography Laboratory, University of Alberta) for X-ray crystallographic analysis of compound 6a.
Angenechem offers custom synthesis of chemicals that are not commercially available:
© 2019 Angene International Limited. All rights Reserved.