200,000+ products from a single source!
sales@angenechem.com
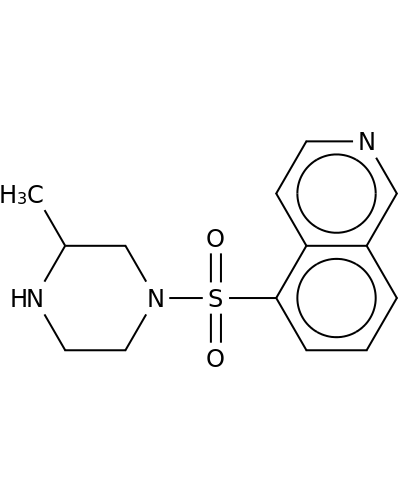
84477-73-6 | Isoquinoline,5-[(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)sulfonyl]-
CAS No: 84477-73-6 Catalog No: AG004W1M MDL No:
Product Description
Catalog Number:
AG004W1M
Chemical Name:
Isoquinoline,5-[(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)sulfonyl]-
CAS Number:
84477-73-6
Molecular Formula:
C14H17N3O2S
Molecular Weight:
291.3687
IUPAC Name:
5-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)sulfonylisoquinoline
InChI:
InChI=1S/C14H17N3O2S/c1-11-10-17(8-7-16-11)20(18,19)14-4-2-3-12-9-15-6-5-13(12)14/h2-6,9,11,16H,7-8,10H2,1H3
InChI Key:
QGSCXAWTTISKLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
SMILES:
CC1NCCN(C1)S(=O)(=O)c1cccc2c1ccnc2
NSC Number:
683547
Properties
Complexity:
434
Compound Is Canonicalized:
Yes
Covalently-Bonded Unit Count:
1
Defined Atom Stereocenter Count:
0
Defined Bond Stereocenter Count:
0
Exact Mass:
291.104g/mol
Formal Charge:
0
Heavy Atom Count:
20
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count:
5
Hydrogen Bond Donor Count:
1
Isotope Atom Count:
0
Molecular Weight:
291.369g/mol
Monoisotopic Mass:
291.104g/mol
Rotatable Bond Count:
2
Topological Polar Surface Area:
70.7A^2
Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count:
1
Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count:
0
XLogP3:
1
Literature
| Title | Journal |
|---|---|
| Synergy between sulforaphane and selenium in the induction of thioredoxin reductase 1 requires both transcriptional and translational modulation. | Carcinogenesis 20030301 |
| Sustained ER Ca2+ depletion suppresses protein synthesis and induces activation-enhanced cell death in mast cells. | The Journal of biological chemistry 20020419 |
| Three-dimensional collagen regulates collagen gene expression by a mechanism that requires serine/threonine kinases and is independent of mechanical contraction. | Biochemical and biophysical research communications 20010112 |
| Isoquinolinesulphonamide derivatives inhibit transcriptional elongation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in a promyelocytic model of latency. | Antiviral chemistry & chemotherapy 19990901 |
| Regulation of the Ah gene battery via Ah receptor-dependent and independent processes in cultured adult rat hepatocytes. | Drug metabolism and disposition: the biological fate of chemicals 19950601 |
Related Products
© 2019 Angene International Limited. All rights Reserved.