200,000+ products from a single source!
sales@angenechem.com
Home > Sulfanilamide > 1576-37-0
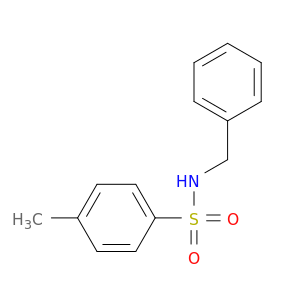
1576-37-0 | Benzenesulfonamide, 4-methyl-N-(phenylmethyl)-
CAS No: 1576-37-0 Catalog No: AG001PJF MDL No:MFCD00159328
Product Description
Catalog Number:
AG001PJF
Chemical Name:
Benzenesulfonamide, 4-methyl-N-(phenylmethyl)-
CAS Number:
1576-37-0
Molecular Formula:
C14H15NO2S
Molecular Weight:
261.3394
MDL Number:
MFCD00159328
IUPAC Name:
N-benzyl-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
InChI:
InChI=1S/C14H15NO2S/c1-12-7-9-14(10-8-12)18(16,17)15-11-13-5-3-2-4-6-13/h2-10,15H,11H2,1H3
InChI Key:
WTHKAJZQYNKTCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
SMILES:
Cc1ccc(cc1)S(=O)(=O)NCc1ccccc1
NSC Number:
37123
Properties
Complexity:
333
Compound Is Canonicalized:
Yes
Covalently-Bonded Unit Count:
1
Defined Atom Stereocenter Count:
0
Defined Bond Stereocenter Count:
0
Exact Mass:
261.082g/mol
Formal Charge:
0
Heavy Atom Count:
18
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count:
3
Hydrogen Bond Donor Count:
1
Isotope Atom Count:
0
Molecular Weight:
261.339g/mol
Monoisotopic Mass:
261.082g/mol
Rotatable Bond Count:
4
Topological Polar Surface Area:
54.6A^2
Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count:
0
Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count:
0
XLogP3:
2.7
Literature
| Title | Journal |
|---|---|
| Paying the piper: the cost of Ca2+ pumping during the mating call of toadfish. | The Journal of physiology 20111115 |
| Patterned femtosecond-laser ablation of Xenopus laevis melanocytes for studies of cell migration, wound repair, and developmental processes. | Biomedical optics express 20110801 |
| Disrupted membrane structure and intracellular Ca²⁺ signaling in adult skeletal muscle with acute knockdown of Bin1. | PloS one 20110101 |
| Synthesis and SAR studies of 1,4-benzoxazine MenB inhibitors: novel antibacterial agents against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. | Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 20101101 |
| N-Benzyl-N-ethyl-4-methyl-benzene-sulfonamide. | Acta crystallographica. Section E, Structure reports online 20101001 |
| Second harmonic generation microscopy probes different states of motor protein interaction in myofibrils. | Biophysical journal 20100922 |
| Muscle-specific inositide phosphatase (MIP/MTMR14) is reduced with age and its loss accelerates skeletal muscle aging process by altering calcium homeostasis. | Aging 20100801 |
| Is the cross-bridge stiffness proportional to tension during muscle fiber activation? | Biophysical journal 20100602 |
| Skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling is independent of a conserved heptad repeat motif in the C-terminus of the DHPRbeta(1a) subunit. | Cell calcium 20100601 |
| Contraction-related stimuli regulate GLUT4 traffic in C2C12-GLUT4myc skeletal muscle cells. | American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 20100501 |
| ATP consumption by sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pumps accounts for 50% of resting metabolic rate in mouse fast and slow twitch skeletal muscle. | American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 20100301 |
| Loss of Smyhc1 or Hsp90alpha1 function results in different effects on myofibril organization in skeletal muscles of zebrafish embryos. | PloS one 20100101 |
| Glycolysis in contracting rat skeletal muscle is controlled by factors related to energy state. | The Biochemical journal 20090513 |
| A myosin II ATPase inhibitor reduces force production, glucose transport, and phosphorylation of AMPK and TBC1D1 in electrically stimulated rat skeletal muscle. | American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 20090501 |
| The effect of myofilament compliance on kinetics of force generation by myosin motors in muscle. | Biophysical journal 20090121 |
| Defective glycinergic synaptic transmission in zebrafish motility mutants. | Frontiers in molecular neuroscience 20090101 |
| The energetic cost of activation in mouse fast-twitch muscle is the same whether measured using reduced filament overlap or N-benzyl-p-toluenesulphonamide. | Acta physiologica (Oxford, England) 20080801 |
| Causes of excitation-induced muscle cell damage in isometric contractions: mechanical stress or calcium overload? | American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 20070601 |
| Energy conservation attenuates the loss of skeletal muscle excitability during intense contractions. | American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 20070301 |
| Mechanical load plays little role in contraction-mediated glucose transport in mouse skeletal muscle. | The Journal of physiology 20070301 |
| Voltage-dependent calcium influx mediates maturation of myofibril arrangement in ascidian larval muscle. | Developmental biology 20070115 |
| Effects of BTS (N-benzyl-p-toluene sulphonamide), an inhibitor for myosin-actin interaction, on myofibrillogenesis in skeletal muscle cells in culture. | Zoological science 20061101 |
| Cross bridges account for only 20% of total ATP consumption during submaximal isometric contraction in mouse fast-twitch skeletal muscle. | American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 20060701 |
| Measurement of activation energy and oxidative phosphorylation onset kinetics in isolated muscle fibers in the absence of cross-bridge cycling. | American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 20060601 |
| Microsphere-based protease assays and screening application for lethal factor and factor Xa. | Cytometry. Part A : the journal of the International Society for Analytical Cytology 20060501 |
| The effects of the myosin-II inhibitor N-benzyl-p-toluene sulphonamide on fatigue in mouse single intact toe muscle fibres. | Acta physiologica (Oxford, England) 20060101 |
| N-Benzyl-p-toluene sulphonamide allows the recording of trains of intracellular action potentials from nerve-stimulated intact fast-twitch skeletal muscle of the rat. | Experimental physiology 20051101 |
| Inhibition of cross-bridge formation has no effect on contraction-associated phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in mouse skeletal muscle. | American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 20050401 |
| Cardiac troponin C (TnC) and a site I skeletal TnC mutant alter Ca2+ versus crossbridge contribution to force in rabbit skeletal fibres. | The Journal of physiology 20050201 |
| Effects of a myosin-II inhibitor (N-benzyl-p-toluene sulphonamide, BTS) on contractile characteristics of intact fast-twitch mammalian muscle fibres. | Journal of muscle research and cell motility 20050101 |
| The action potential-evoked sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release is impaired in mdx mouse muscle fibres. | The Journal of physiology 20040515 |
| Cross-bridge blocker BTS permits direct measurement of SR Ca2+ pump ATP utilization in toadfish swimbladder muscle fibers. | American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 20031001 |
| Mechanism of inhibition of skeletal muscle actomyosin by N-benzyl-p-toluenesulfonamide. | Biochemistry 20030527 |
| Skeletal muscle myosin cross-bridge cycling is necessary for myofibrillogenesis. | Cell motility and the cytoskeleton 20030501 |
| A small-molecule inhibitor of skeletal muscle myosin II. | Nature cell biology 20020101 |
Related Products
© 2019 Angene International Limited. All rights Reserved.