200,000+ products from a single source!
sales@angenechem.com
Home > Pyridines > 115900-75-9
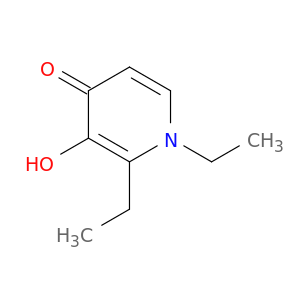
115900-75-9 | 4(1H)-Pyridinone, 1,2-diethyl-3-hydroxy-
CAS No: 115900-75-9 Catalog No: AG000H2X MDL No:MFCD00869703
Product Description
Catalog Number:
AG000H2X
Chemical Name:
4(1H)-Pyridinone, 1,2-diethyl-3-hydroxy-
CAS Number:
115900-75-9
Molecular Formula:
C9H13NO2
Molecular Weight:
167.2050
MDL Number:
MFCD00869703
IUPAC Name:
1,2-diethyl-3-hydroxypyridin-4-one
InChI:
InChI=1S/C9H13NO2/c1-3-7-9(12)8(11)5-6-10(7)4-2/h5-6,12H,3-4H2,1-2H3
InChI Key:
XIYFEESCIBNMIC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
SMILES:
CCc1c(O)c(=O)ccn1CC
UNII:
G3PX21X7IU
Properties
Complexity:
253
Compound Is Canonicalized:
Yes
Covalently-Bonded Unit Count:
1
Defined Atom Stereocenter Count:
0
Defined Bond Stereocenter Count:
0
Exact Mass:
167.095g/mol
Formal Charge:
0
Heavy Atom Count:
12
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count:
3
Hydrogen Bond Donor Count:
1
Isotope Atom Count:
0
Molecular Weight:
167.208g/mol
Monoisotopic Mass:
167.095g/mol
Rotatable Bond Count:
2
Topological Polar Surface Area:
40.5A^2
Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count:
0
Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count:
0
XLogP3:
1.3
Literature
| Title | Journal |
|---|---|
| Identifying chelators for metalloprotein inhibitors using a fragment-based approach. | Journal of medicinal chemistry 20110127 |
| Induction of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF-1α) in rat kidneys by iron chelation with the hydroxypyridinone, CP94. | Biochimica et biophysica acta 20110101 |
| An in vitro comparison of the effects of the iron-chelating agents, CP94 and dexrazoxane, on protoporphyrin IX accumulation for photodynamic therapy and/or fluorescence guided resection. | Photochemistry and photobiology 20110101 |
| The hydroxypyridinone iron chelator CP94 can enhance PpIX-induced PDT of cultured human glioma cells. | Photochemistry and photobiology 20100101 |
| Pretreatment to enhance protoporphyrin IX accumulation in photodynamic therapy. | Dermatology (Basel, Switzerland) 20090101 |
| Enhancement of methyl-aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy by iron chelation with CP94: an in vitro investigation and clinical dose-escalating safety study for the treatment of nodular basal cell carcinoma. | Journal of cancer research and clinical oncology 20080801 |
| Clinical investigation of the novel iron-chelating agent, CP94, to enhance topical photodynamic therapy of nodular basal cell carcinoma. | The British journal of dermatology 20080801 |
| Basic 3-hydroxypyridin-4-ones: potential antimalarial agents. | European journal of medicinal chemistry 20080501 |
| Topical applications of iron chelators in photosensitization. | Photochemical & photobiological sciences : Official journal of the European Photochemistry Association and the European Society for Photobiology 20071201 |
| Direct comparison of delta-aminolevulinic acid and methyl-aminolevulinate-derived protoporphyrin IX accumulations potentiated by desferrioxamine or the novel hydroxypyridinone iron chelator CP94 in cultured human cells. | Photochemistry and photobiology 20070101 |
| Biochemical manipulation via iron chelation to enhance porphyrin production from porphyrin precursors. | Journal of environmental pathology, toxicology and oncology : official organ of the International Society for Environmental Toxicology and Cancer 20070101 |
| Spectroscopic and potentiometric characterization of oxovanadium(IV) complexes formed by 3-hydroxy-4-pyridinones. Rationalization of the influence of basicity and electronic structure of the ligand on the properties of V(IV)O species in aqueous solution. | Inorganic chemistry 20061002 |
| Comparing and combining light dose fractionation and iron chelation to enhance experimental photodynamic therapy with aminolevulinic acid. | Lasers in surgery and medicine 20060401 |
| Characterization of two isomeric beta-d-glucosiduronic acids derived from 1,2-diethyl-3-hydroxypyridin-4-one (CP94) in rat liver homogenate incubates. | The Journal of pharmacy and pharmacology 20020701 |
| Iron chelators as therapeutic agents against Pneumocystis carinii. | Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy 19940501 |
Related Products
© 2019 Angene International Limited. All rights Reserved.